Selecting the Ideal Industrial Switch: Managed vs. Unmanaged Comparison
While many articles discuss the differences between managed and unmanaged switches, few look into their applications in the industrial field, like industrial control, manufacturing, energy and power, intelligent transportation, intelligent coal mines, etc,. Generally unmanaged switches are used for data exchange between the internal network of the equipment, such as the CPU and each distributed module, while managed switches are used for communication between the equipment and the plant network. This post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of unmanaged and managed switches in the industrial sector and their key differences. By the end, you'll know how to select the right switch for your industrial network needs.
Unmanaged Industrial Switches
Industrial unmanaged switches offer basic connectivity without the need for complex configuration. These switches are plug-and-play devices, requiring minimal setup and maintenance, making them ideal for applications where simplicity is key. They are cost-effective solutions, suitable for basic network connectivity in simple or non-critical industrial environments.
While unmanaged switches offer simplicity and affordability, they come with limitations. They lack advanced configuration options, remote management capabilities, and built-in diagnostics or monitoring tools. This makes them less suitable for complex industrial networks that require advanced features and remote management functionality. However, for many industrial applications where basic connectivity is sufficient, unmanaged switches provide a reliable and straightforward solution.

Industrial unmanaged switches are cost-effective, durable in harsh environments, and can connect many devices to a network. They offer the benefits of plug-and-play devices, and the configuration and implementation process does not require a network expert. These devices are transparent to most industrial protocols, eliminating compatibility issues. They are usually small and can be very easily installed in control cabinets.
Managed Industrial Switches
Industrial managed switches are advanced networking devices that offer comprehensive control and management capabilities, making them suitable for complex industrial environments. Unlike unmanaged switches, managed switches provide full configuration options, remote management capabilities, and built-in diagnostics and monitoring tools. They also support advanced network protocols, allowing for greater flexibility and customization.

Despite their advanced features, managed switches come with some drawbacks. They typically have a higher upfront cost compared to unmanaged switches and may require more time and expertise to set up and maintain. However, for applications that demand fine-grained control, real-time monitoring, and robust security features, the benefits of managed switches outweigh the initial investment.
Key Considerations When Choosing Between Industrial Managed and Unmanaged Switches
Managed and unmanaged industrial switches differ in various aspects, including controllers and cost. Managed industrial switches have more features than unmanaged industrial switches, but they require specialized knowledge to navigate. A managed switch can better manage the network and data frame traffic that passes through it. Unmanaged industrial switches, on the other hand, have the main basic function of providing connected devices to communicate with each other.
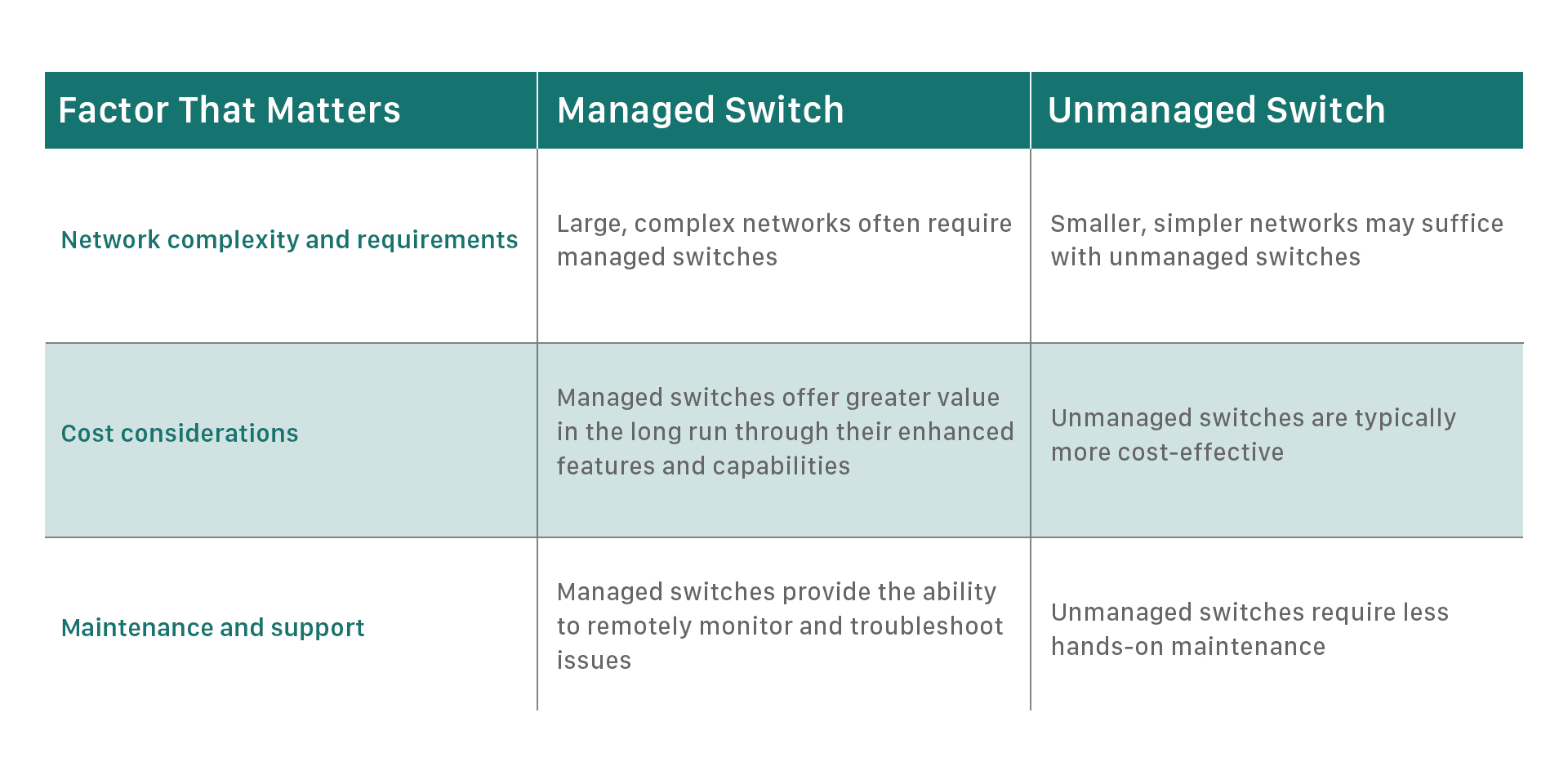
When to Choose Industrial Managed Switch Over Unmanaged Switch
Industrial unmanaged Ethernet switches are transparent "plug and play" network hubs to connect field data to IP networks at sites with harsh environmental conditions. However, once the quantity of interconnected devices like sensors, actuators, PLCs, etc, increases, a network issue may occur. Though issues like traffic overload will delay email or video screaming at home or office, it will impact the running of industrial equipment in the industrial field. Therefore, industrial managed switch should be chosen under the below conditions:
Enhanced Traffic Filter
To minimize network latency and increase the level of certainty in the network, it is necessary to transmit communication packets from the source device to the target device. When packets arrive where they are not needed, the target device consumes resources to process the packets, thus delaying the processing of critical communications. Modern unmanaged switches can implement some level of packet filtering to more or less alleviate this problem. However, unmanaged switches cannot effectively recognize and filter many types of packets, so these devices end up forwarding unwanted packets to all connected devices.
Therefore, we need a managed industrial switch to realize the filtering, because it can:
Multicast Filtering: Multicast packets are common in control systems and are forwarded indiscriminately by unmanaged switches. Managed switches implement Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) to understand when these packets are needed and forward them selectively.
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN): Managed switches provide VLANs so users can logically separate network traffic on the same physical device. This effectively groups devices so that each group does not receive traffic from other groups.
Traffic Priority: Using the Quality of Service (QoS) feature allows the device to prioritize the packets it sends so that the managed switch can process each packet in order based on its priority.
Network Redundancy
Basic unmanaged Ethernet only allows point-to-point connections or paths between the ports of any two devices on the network. On this network, if multiple paths between devices form a loop, packets will loop endlessly in the loop, resulting in a network storm that will sooner or later overwhelm the network. The consequence of a single path, however, is that any hardware, power, or cable failure will result in a communication outage. Redundancy is a significant advantage of managed switches over unmanaged switches. Two common approaches are:
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP): This IT-based protocol allows designers to create multiple paths on a network, thus creating loops, because managed switches can use RSTP to determine and control which path should be used and which alternate path should be switched to detect a failure. This avoids network storms.
Loop Protocol: Loop protocol can be used to connect switches arranged in a ring. It can recover from network failures much faster than RSTP and can be used for many critical industrial applications. Loop protocol is not standardized and can only be implemented using certain brands and models of switches, like MW-ring, the self-developed loop protocol of Maiwe Communication.
Comprehensive Security
For industrial networks that run physical devices and contain valuable data, the need to protect against accidental or malicious activity is critical. Unmanaged switches forward packets, but managed switches can provide additional protection in the following ways:
Port Access Control: Users can disable unused ports to restrict unauthorized access.
Management and Browser Security: These settings include passwords and SSL, which ensures that unauthorized people or applications cannot compromise switch and network settings.
In-Depth Troubleshooting and Diagnosis
When network problems do occur, technicians need to provide information for troubleshooting as soon as possible. Unmanaged switches typically do not support this type of diagnostics, but managed switches can provide the necessary visibility in several ways:
Port Monitoring: For detailed troubleshooting, this feature allows the technician to identify the port to be examined so that all data from that port can be mirrored to another available port. Users can connect their PCs to the mirrored port and use software such as Wireshark to examine the contents of the packets.
Network Statistics: Network statistics are provided in the configuration of the managed switch and users can connect and access them through a web browser, provided they have the proper authorization. The data can help identify corrupted packets, such as those caused by field wiring errors.
Unmanaged switches are a cost-effective and simple way to implement network port expansion capabilities, especially for applications that lack manpower and time. Managed switches are ideal for use in complex networks, critical infrastructure, and applications where reliability, scalability, and security are paramount. They provide the flexibility and control needed to optimize network performance, ensure data integrity, and streamline maintenance processes.
Conclusion
Industrial switches play a crucial role in the seamless operation of industrial networks, facilitating communication between devices and ensuring data flows efficiently. These switches come in two main types: managed and unmanaged. Understanding the differences between these types is vital for making informed decisions when purchasing industrial switches.




















 Pre
Pre
 Back to list
Back to list