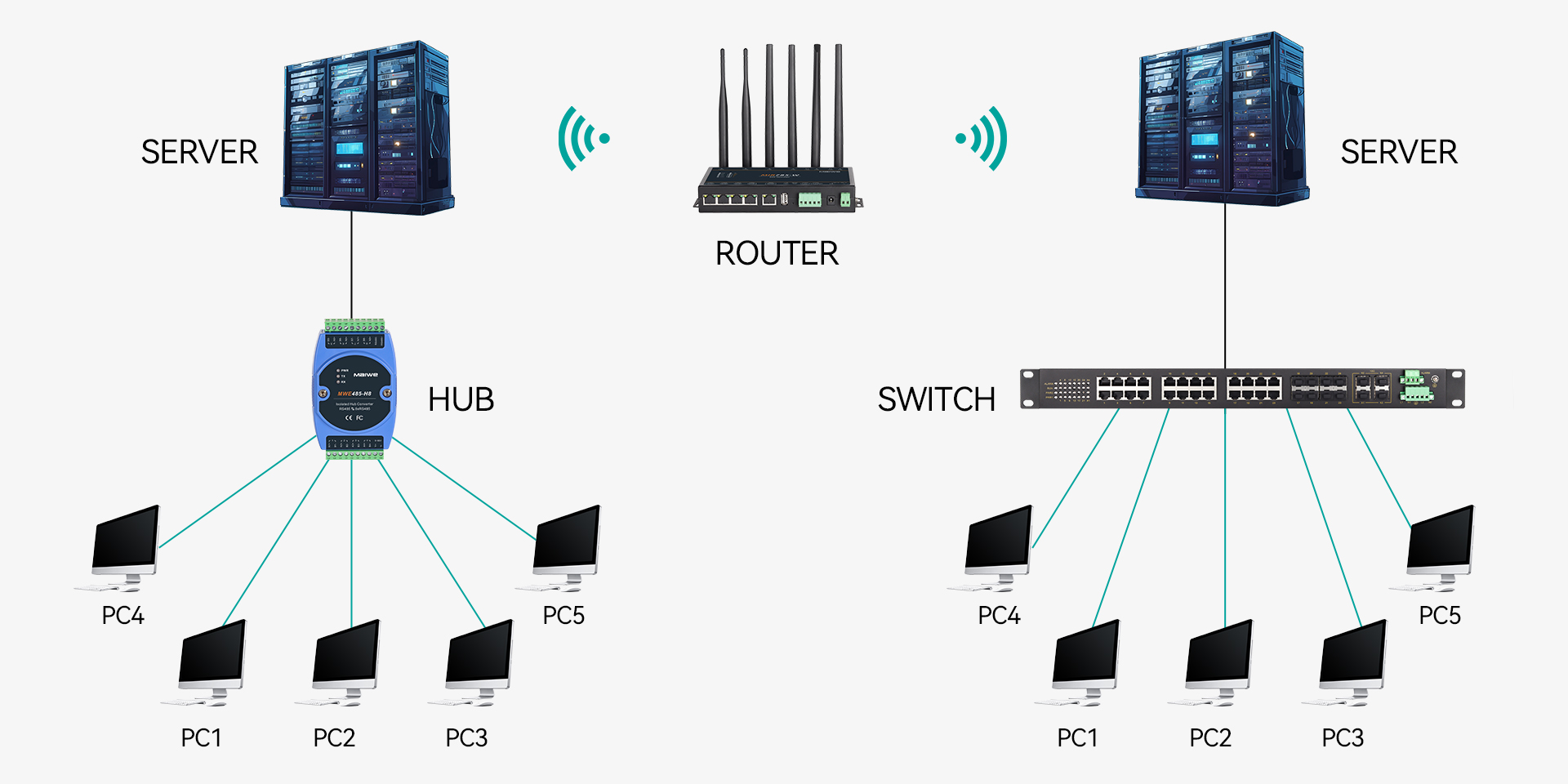
Hub vs Switch vs Router in Industrial Ethernet
In today's world of industrial automation, having strong and reliable communication networks is super important. And at the core of these networks are devices like switches, routers, and hubs. These devices help make sure that data flows smoothly and efficiently. Among them, switches are the most commonly used in industrial settings.In this article, we'll explain these devices in simple terms, and see how these devices all work together to keep industrial networks running smoothly.
Hub
A hub works at the basic level of a network, called the physical layer. It's like a messenger that takes a message and delivers it to everyone it knows without checking who actually needs the message. This means that when a device sends data through a hub, the hub sends that data to all devices connected to it, whether they need it or not. This can lead to network congestion and wasted bandwidth, which is not ideal. Moreover, a hub operates in half-duplex mode, meaning that it can either send or receive data, but not both simultaneously.
Since hubs don't filter or check who gets the data, they're not very secure. Because of this, they're not commonly used in modern networks where security is a big concern. However, there are still some special cases where hubs are needed, like when you need to capture all the messages on a network for analysis.
Switch
A switch is like a smart traffic controller for data in a network. It works at a layer called the data link layer, which is like its own neighborhood in the network world. A switch operates in full-duplex mode, allowing it to send and receive data simultaneously. This means that a switch can handle data traffic more efficiently than a hub. There are two main types of industrial switches: unmanaged and managed.
Unmanaged switches are the basic type. They simply take data from one device and send it to the specific device that needs it. They use something called MAC addresses, which are like unique IDs for devices, to figure out where to send the data.
Managed switches, on the other hand, are like the supercharged version. They can do a lot more than just basic data forwarding. They can manage the network better and support more fancy features. For example, they can help you figure out how devices are connected to each other (using LLDP), keep an eye on the network (using SNMP), and even divide the network into smaller parts (using VLANs) to keep things organized.

In industrial networks, it's important to use industrial switches instead of commercial ones. Industrial switches are built to handle the tough conditions of industrial environments and are more reliable. Plus, they often have more advanced features that are useful in industrial settings.
Overall, switches are like the traffic directors of a network, making sure data gets where it needs to go efficiently and securely.
Router
A router is a key part of an industrial ethernet network. It works at the heart of the network layer, which is layer 3 of the OSI network reference model. Think of it as a bridge connecting two separate networks, allowing devices on one network to communicate with those on another.
Routers have two main types of ports: LAN ports and WAN ports. LAN ports are used to connect to a local area network, which is a network within a small area like a factory floor or an office. WAN ports, on the other hand, connect to a wide area network or to another subnet. This means they can link to networks that span larger distances, like connecting different buildings or locations.

Inside a router, there's a special table called a routing table. This table keeps track of which ports and devices are connected to which networks. But unlike a switch, a router uses IP addresses to decide where to send messages. If a device on one subnet wants to send a message to a device on another subnet, it sends the message to the router (by setting the gateway address). The router then looks at its routing table to figure out the best way to get the message to its destination.
Routers are really powerful. They support a lot of different network protocols, like TCP/IP, DHCP, ICMP, and more. This means they can handle a wide range of network tasks. Plus, some routers have extra features like firewalls and VPN capabilities to help keep the network safe and secure.
In a factory setting, industrial routers are crucial for the upper management system, like MES (Manufacturing Execution System). They help make sure all the different parts of the network can talk to each other smoothly, keeping the factory running efficiently. So, whether it's a small office or a large industrial complex, routers are an essential part of any modern network.
Conclusion
In an industrial ethernet system, routers, switches, and hubs work together to ensure smooth and efficient communication between various devices and subnets. When these three devices work together, they form a powerful and flexible network infrastructure. The hub provides basic connectivity for local devices, the switch enhances performance by directing traffic efficiently, and the router ensures seamless communication between subnets and external networks. This synergy ensures that industrial ethernet runs smoothly, enabling efficient data transmission and device communication across the entire network.




















 Pre
Pre
 Back to list
Back to list